Sending Data
To be able to add data, you must create a file structure and add a column mapping. A column mapping is a list of columns describing a document(.CSV, .XLSX, .XLS).
To add a column mapping, you must first define the file structure:
filestructure = FileStructure(
file_type=FileType.xlsx,
charset="UTF-8",
delimiter=",",
quote_char='"',
escape_char='\\',
eol_char="\\r\\n",
comment_char="#",
header=True,
sheet_name="Sheet1"
)
It is important to note that aside from the file_type(which can be set to CSV, XLSX or XLS) and
the sheet_name(which is optional), the attributes above are set by default.
That means that unless the value of your attribute is different, you do not need to set it.
Now, a column mapping can be created:
column_list = [
Column('<Column name>', <Column index>, <Column Type>),
Column('<Column name>', <Column index>, <Column Type>),
Column('<Column name>', <Column index>, <Column Type>, time_format='<Your time format>')
]
column_mapping = ColumnMapping(column_list)
Column nameis the name of the column.Column indexis the index of the column of your file. Note that the column index starts at 0.Colulmn Typeis the type of the column. It can beCASE_ID,TASK_NAME,TIME,METRIC(a numeric value) orDIMENSION(can be a string).
Please note that your time format must use the Java SimpleDateFormat format.
This means you must mark the date by using the following letters (according to your date format):
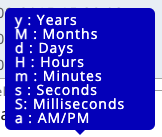
For example, your date format may look like this:
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS
In the following examples, do not forget to change the time_format before using the code.
It is also possible to check whether a column mapping exists or not:
my_project.column_mapping_exists
Furthermore, a column can also be created from a JSON.
json_str = '{"name": "test", "columnIndex": "1", "columnType": "CASE_ID"}'
column = Column.from_json(json_str)
Therefore, a Column Mapping can also be created from a JSON column dictionary. For example:
column_dict = '''{
"col1": {"name": "case_id", "columnIndex": "0", "columnType": "CASE_ID"},
"col2": {"name": "task_name", "columnIndex": "1", "columnType": "TASK_NAME"},
"col3": {"name": "time", "columnIndex": "2", "columnType": "TIME", "format": "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm"}
}'''
column_mapping = ColumnMapping.from_json(column_dict)
The Column Mapping can also be created from a JSON column list. The major difference between the list and the dictionary is that in the dictionary you have to enunciate the column number before giving the other informations.
column_list = '''[
{"name": "case_id", "columnIndex": "0", "columnType": "CASE_ID"},
{"name": "task_name", "columnIndex": "1", "columnType": "TASK_NAME"},
{"name": "time", "columnIndex": "2", "columnType": "TIME", "format": "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm"}
]'''
column_mapping = ColumnMapping.from_json(column_list)
Moreover, it is possible to return the JSON dictionary format of the Column with the to_dict() method.
By doing that, we can then create a Column Mapping with the from_json() method.
The json.dumps() function will convert a subset of Python objects into a JSON string.
column_list = [
Column('case_id', 0, ColumnType.CASE_ID),
Column('task_name', 1, ColumnType.TASK_NAME),
Column('time', 2, ColumnType.TIME, time_format="yyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm")
]
column_mapping = ColumnMapping(column_list)
json_str = json.dumps(column_mapping.to_dict())
column_mapping = ColumnMapping.from_json(json_str)
After creating it, the column mapping can be added:
my_project.add_column_mapping(filestructure, column_mapping)
Finally, you can add CSV, XLSX or XLS files:
wg = Workgroup(w_id, w_key, api_url, auth_url)
p = Project("<Your Project ID>", wg.api_connector)
filestructure = FileStructure(
file_type=FileType.xlsx,
sheet_name="Sheet1"
)
column_list = [
Column('Case ID', 0, ColumnType.CASE_ID),
Column('Start Timestamp', 1, ColumnType.TIME, time_format="yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm"),
Column('Complete Timestamp', 2, ColumnType.TIME, time_format="yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm"),
Column('Activity', 3, ColumnType.TASK_NAME),
Column('Ressource', 4, ColumnType.DIMENSION),
]
column_mapping = ColumnMapping(column_list)
p.add_column_mapping(filestructure, column_mapping)
p.add_file("ExcelExample.xlsx")
Furthermore, grouped tasks can also be declared if needed. If a grouped task is created in a column, there must be grouped tasks declared in other columns as well as they cannot function individually:
column_list = [
Column('case_id', 0, ColumnType.CASE_ID),
Column('time', 1, ColumnType.TIME, time_format="yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm"),
Column('task_name', 2, ColumnType.TASK_NAME, grouped_tasks_columns=[1, 3]),
Column('country', 3, ColumnType.METRIC, grouped_tasks_aggregation=MetricAggregation.FIRST),
Column('price', 4, ColumnType.DIMENSION, grouped_tasks_aggregation=GroupedTasksDimensionAggregation.FIRST)
]
column_mapping = ColumnMapping(column_list)
The grouped_tasks_columns represent the list of column indices that must be grouped.
If grouped_tasks_columns is declared, it has to at least have the index of a column of type TASK_NAME
and the index of a column of type METRIC, DIMENSION or TIME. It must not have the index of a column of type CASE_ID.
The grouped_tasks_aggregation represents the aggregation of the grouped tasks.
Moreover, if a grouped task aggregation's column type is METRIC, then the grouped task's type must be of MetricAggregation type.
Similarly, if a grouped task aggregation's column type is DIMENSION, then the grouped task's type must be of GroupedTasksDimensionAggregation type.
Finally, if grouped_tasks_columns is declared, the column's type must be TASK_NAME.